Many storage tanks at present in use within the chemical and associated industries are designated as "atmospheric" storage vessels. This paper promises a abstract of the design specifications for low-pressure storage tanks above all referring to the design and sizing of strain aid systems. The numerous strain aid circumstances relevant to storage tanks are thought of and the suitable sizing calculations mentioned with a purpose to supply risk-free venting of the system.
Various varieties of strain reduction preparations are described and their software to differing course of situations and elements is discussed. The key variations between the varied varieties of strain reduction instruments and methods are highlighted when it comes to the relevance to the storage of flammable and poisonous materials. The design and use of nitrogen purging and padding and flame arresters on vents can additionally be examined. Liquid actions are usually not the one issues for tank venting. Overpressure and vacuum failure can appear as a tank is heated up/cooled down, respectively. These thermal results of the tank rely upon the dimensions of the tank, the situation of the tank — hotter versus colder climates can change the vapor within the tank — and in addition the quantity of insulation the tank has.
Insulated tanks are extra immune to temperature changes, which thus reduces the quantity of movement required by the vents. This discount component is dependent upon the properties of the insulation — resembling the thermal conductivity and heat-transfer coefficient with typical values included in API 2000 — in addition to the thickness of the insulation material. In the case of in-breathing , tanks stored at larger temperatures could very effectively be cooled by the surroundings at a speedier price than they are often heated. The design case for cooling and inbreathing is when a heat tank on a sizzling day is quickly cooled by a sudden rainstorm. Condensable product vapors can even raise the cooling result on storage tanks; each of those are accounted for in API 2000.
These thermal effects, along with the liquid actions of the tanks, are thought-about minimal necessities for the venting circulate rates. The complete venting requirement assumes these two to behave concurrently and sums the circulate necessities of each. This work determines the traditional and emergency venting necessities for atmospheric storage tank in a fuel plant utilizing ASPEN HYSYS Safety environment. Pressure comfort sizing calculations are carried out for hearth case scenario. Since Aspen HYSYS trustworthy practices atmosphere is supplied with up to date industrial design commonplace codes like API 650, API 620 and API 2000, the outcomes of this learn are dependable and accurate. The methodology developed on this work is beneficial to course of design engineers to in a timely fashion analyze the low-pressure storage tank protection.
The set factors of the vents can be presented by weight loading, spring loading or buckling pin. Both fuel stations are regarded to be high-volume, in view that they dispense greater than 3.6 million gallons of gasoline per year,26 and gasoline was saved in underground storage tanks , which is typical within the US. Both fuel stations had Stage II vapor restoration mounted applying the vacuum-assist method.
In that method, gasoline vapors, which might be ejected into the ambiance as a working loss throughout refueling of buyer car tanks, are collected on the vehicle/nozzle interface by a vacuum pump. The recovered vapors are then directed by way of a coaxial hose again into the mixed storage tank ullage of the fuel station. Stage I vapor restoration was additionally used at equally fuel stations throughout gasoline deliveries. Both websites had a 3-inch diameter (7.5 cm) single above-grade vent pipe with below-grade manifold that related the vent strains from a number of USTs; the cracking pressures of the P/V valves have been set to +3 and −8 iwc (+7.5 and −20 hPa). If unstable liquids are stored, the consequences of warmth or fuel ensuing from polymerization, decomposition, condensation, or self-reactivity shall be taken into account.
The complete ability of equally common and emergency venting gadgets shall be not lower than that derived from Table FL-16 besides as offered in or . Such system could be a self-closing manhole cover, or one applying lengthy bolts that let the duvet to carry beneath inner pressure, or a further or bigger reduction valve or valves. The wetted location of the tank shall be calculated on the idea of fifty five percent of the whole uncovered location of a sphere or spheroid, seventy five percent of the whole uncovered location of a horizontal tank and the primary 30 ft above grade of the uncovered shell location of a vertical tank. If unstable liquids are stored, it's essential to consider the consequences of warmth or fuel ensuing from polymerization, decomposition, condensation, or self-reactivity. The complete ability of equally common and emergency venting gadgets have to be not lower than that derived from Table H-10 besides as offered in and of this subsection. You ought to calculate the wetted location of the tank on the idea of 55% of the whole uncovered location of a sphere or spheroid, 75% of the whole uncovered location of a horizontal tank and the primary thirty ft above grade of the uncovered shell location of a vertical tank.
The problem with such a system is to make convinced that the bladder tank ability just isn't exceeded by the gasoline evaporation rate. Therefore, present CARB setback distances is perhaps satisfactory for fuel stations in California however much less so for the opposite forty nine US states, and different countries—depending on air pollution prevention technologies requirements. The use of Pressure and Vacuum Relief Valves is remitted by just about all the acknowledged regulatory establishments concerned in tank safety, resembling API, OSHA, NFPA etc.
API 12F, Section 6, additional stipulates using Emergency Pressure Relief Vents, besides PVRV's when storage tanks containing flammable liquids are uncovered to fire, until the tanks in query are set up in distant locations. The venting system have to be designed in accordance to API 2000 which provides the rigorous formulation to calculate each regular venting and emergency venting. Annex B and C of API 12 F present "short cut" tables with values for thermal venting and emergency venting for various tank sizes, respectively.
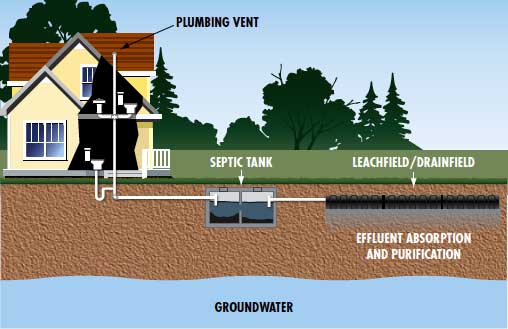
Recently, multiplied environmental considerations and regulation have made appropriate storage tank venting a priority. One of the ingredients of a tank venting system is the Pressure and Vacuum Relief Valve . Pressure and Vacuum Relief Valves safeguard tanks towards rupture because of will escalate in inner strain or imploding because of vacuum, thus avoiding everlasting harm to the equipment.
Fixed roof tanks are vulnerable to rupture from many situations consisting of each time liquid is pumped into the tank or on account of ameliorations within the vapor strain of the contents, attributable to important thermal changes. During these instances, the PVRV protects the tanks from over-pressure by depressurizing the tank. Alternately, imploding of a tank could take place for numerous reasons, consisting of the pumping out process or on account of thermal changes.
This is as a outcome of indisputable incontrovertible verifiable truth that because the liquid degree inside the tank decreases, the strain inside the vapor area additionally decreases making a vacuum. The vacuum can solely be damaged by permitting both atmospheric air, an inert fuel reminiscent of Nitrogen, or blanket fuel to enter the tank. PVRVs often vent to environment however can even have provisions to permit the vapors to be piped away for recuperation or destruction. Overpressure is a time period which can convey nightmares to tank owners, operators and engineers alike. Too a lot strain buildup in a tank may trigger it to rupture, leading to lack of containment, improved probability of fireside and probably lack of life. Too little strain can create a vacuum inside a tank, inflicting it to implode and leading to comparable however inside the main much less extreme effects.
To alleviate these strain changes, storage tanks are required to have vents that may permit inner vapors to flee in addition to permit air to fill within the tank . Recently, API 2000 — the governing commonplace for tank venting specifications — launched a extra exact technique of figuring out the movement requirements. However, these new provisions supply further degrees of complexity within the computations and stay an enigma to these that are accustomed to the previous venting calculations .
This article sheds mild on these new specifications so they can stop catastrophic failures inside the future. You need to take desirable means to stop the buildup of flammable liquids beneath adjoining liquefied petroleum fuel containers similar to by diversion curbs or grading. When flammable liquid storage tanks are inside a diked area, the liquefied petroleum fuel containers should be outdoors the diked region and no less than ten ft away from the centerline of the wall of the diked area.
The foregoing provisions should not apply when liquefied petroleum fuel containers of one hundred twenty five gallons or much much much less capability are put in adjoining to gasoline oil provide tanks of 550 gallons or much much much less capacity. This conjecture is in step with typical US storage tank volumes (~10,000 to 30,000 gal). Assuming that Phase I vapor recuperation didn't work in any respect and that 10,000 gal (~38,000 L) of gasoline have been delivered, the working loss (volume of gasoline vapor/air combination launched to the ambiance with the aid of the vent pipe) is 38,000 L. It can be affordable to imagine that provide lasted below one hour. According to Table 2, the utmost hourly circulation price with the aid of the vent pipe was 250 L/min at GS-MW, which might end in a most cumulative vapor launch of 15,000 L inside this hour.
How To Calculate Vent Size The measured optimum cumulative launch underestimates the assumed working lack of 38,000 L. This might possibly be attributable to a gasoline delivery, which concerned dropping gasoline from a number of compartments of a tanker truck, with the vapor return hose not being accurately attached for less than many of the emptied compartments. Process vessels and storage tanks containing liquid and fuel can every now and then be subjected to accumulate of overpressure attributable to couple of motives – liquid movement coming into the tank and thus compressing the fuel thermal enlargement of the fluids contained within the tank. Due to those couple of reasons, the resultant quantity enlargement of gases within the tank results in accumulate of pressure.
Overpressure within the tank can cause manageable structural damages and equipments must be protected in opposition to such possibility. Protection could be supplied by the use of an open vent or a respiration valve. These units will enable air to move out, thus stopping strain construct up within the tank.
The minimal required venting circulation for the outbreathing should be calculated making use of tips from API 2000. Different potential situations with the corresponding pattern venting calculations are mentioned within the next sections. Since Aspen HYSYS dependable practices setting is supplied with up to date industrial design normal codes like API 650, API 620 and API 2000, the outcomes of this learn are dependable and ... Vent pipes need to discharge solely upward as a way to disperse vapors. Vent pipes 2 inches or much less in nominal inside diameter need to not be obstructed by units which will trigger extreme to come back pressure.
Vent pipe retailers should be positioned in order that flammable vapors can not enter constructing openings, or be trapped underneath eaves or different obstructions. Vent pipe emissions of benzene have been modeled at a 1-hour temporal decision as described in Section 2.4. However, they don't seem to be the only supply of gasoline emissions at fuel stations. In Section A of Supporting Material, we element how these different emission sources have been modeled. Note that the vent pipe losses are a lot larger than different losses.
Figure 2 reveals the time-series info for the volumetric circulation price Q of the gasoline vapor/air combination by the vent pipe and tank strain p that we collected on the 2 fuel stations. At GS-MW, little vapor was traditionally launched within the late evening and within the very early morning, whereas releases have been often a lot larger within the course of the daytime and evenings, presumably when extra gasoline was allotted . While we will not have entry to time of gasoline supply records, area visits point out that point durations with no releases coincide with gasoline deliveries. For instance, gasoline supply in all likelihood occurred on January 6 at 7 pm (see Figure 3a; an amplification of knowledge proven in Figure 2a). As a result, the UST strain dropped by about 10 hPa, far under the cracking strain of the P/V valve.
The decreased fuel strain within the ullage improved till the cracking strain of the P/V valve was reached. A very small vapor launch (~2 L/min) was noticed briefly on the subsequent day at 2 am. The vapor move price turns into comparatively considerable again, ~12 L/min, solely after 6 am, i.e., eleven hours after gasoline delivery. These vent pipes are put in place to equilibrate pressures within the tanks and may be positioned as shut as just a few meters from residential buildings in dense city settings .
At GS-NW, vent pipe releases occurred a lot of the time, within the course of the daytime when gasoline was allotted and at evening when the fuel station was closed. Vent releases have been greater when the fuel station was closed, suggesting that within the day-time Stage II vapor recuperation resulted within the injection of vapors into the storage tank that weren't absolutely equilibrated with the liquid gasoline. During night-time, the gradual equilibration of unsaturated air within the ullage of the UST with gasoline vapors might then have induced exceedance of the cracking strain of the P/V valve and consequently vapor release. It appears counterintuitive that much less nighttime emissions occurred on the fuel station the place gasoline was dispensed. However, at the same time gasoline is being dispensed, the outgoing liquid creates further ullage volume, and counting on extra air ingestion rate, a adverse strain might outcome that lowers vent pipe emissions.
Vapors inside atmospheric and low-pressure storage tanks could condense both slowly within the time of rainfalls or abruptly as an example by injection of chilly liquid within the time of steaming. Vapor condensation inside tanks could induce deformation and collapse. The newest editions of API 2000 and ISO requirements lack an specific formulation for the required in-breathing to compensate for vapor condensation, as a consequence of a protracted rainfall, which is the primary matter of this paper. The analytical mannequin here, which incorporates vapor condensation on the tank walls, predicted complete in-breathing requirements for mixtures of air saturated with vapors, that are considerably bigger than these calculated utilizing the procedures within the standards. This paper is aimed to supply some practical steerage for the reader addressing the difficulty of vapor condensation when identifying the worst practical case state of affairs for the tank respiration requirements.
Storage Tanks are an vital section of a petroleum Industry, This software program is predicated on the API Std. 2000, which calculates the design of Venting and its ability for low strain storage & atmospheric storage tanks in case of usual venting, attributable to thermal changes, and in case of fireside exposure. Require vents to forestall strain changes, which might in any different case outcome from temperature modifications and the withdrawal or the addition of liquid.
API Standard 2000, venting atmospheric and Low Pressure Storage Tanks, offers useful guidelines for vent design. The principals of this normal should be utilized to fluids apart from petroleum products. Excessive losses of risky liquids, especially these with flash factors under one hundred °F (38 °C), might end result from using open vents on mounted roof tanks. Sometimes vents are manifolded and led to a vent tank, or the vapor could also be extracted by a restoration system. Vacuum collapse causes many accidents involving gear with low strain scores resembling atmospheric storage tanks and bins. This paper presents techniques to determine the suitable aid capacities and specify strain aid gadgets to guard atmospheric storage tanks and different related gear towards this hazard.
Calculations are primarily based on elementary warmth stability and fluid circulate calculations. Data for this learn have been obtained from vent launch measurements carried out at two fuel stations as section of technical help to the fuel stations to quantify gasoline vapor losses by means of the vent pipes of their storage tanks. A motivation for conducting the measurements was to carry out a cost-benefit evaluation to match the financial losses as a result of misplaced gasoline versus the price of applied sciences that scale down the emissions. The precise location of the 2 fuel stations is simply not revealed for confidentiality reasons.
The fuel station managers and employees who approved the gathering and evaluation of those facts haven't been concerned within the present manuscript. The PVRV is usually put in on a flanged nozzle on the highest of the fastened roof of an atmospheric or low strain storage tank. Besides defending the gear from everlasting damage, PVRVs additionally serve to attenuate emissions to the environment, in addition to decrease lack of product attributable to evaporation, by controlling tank venting. When mixed with a well-designed vapor restoration system, the lack of product might be minimize to pretty much zero, thus resulting in important funds savings, chiefly for tank farms.
These gadgets additionally assist lessen corrosion of the encompassing tools on account of much less fugitive emissions. Therefore, the price of total plant preservation is additionally decreased. At Poly Processing we observed an excessive amount of injury to tanks from over pressurization. So, a number of years ago, Poly Processing commissioned a 3rd social gathering engineering agency to review the influence of strain on pneumatically crammed chemical storage tanks on account of totally different purposes or settings. The prevailing trade commonplace with regards to venting was to make use of a vent one inch bigger than the fill line; for example, a two-inch fill line requires a three-inch vent. The examine decided the usual to be satisfactory is pumped mechanically.
However, bulk storage tanks are sometimes pumped off a tanker truck utilizing air. As the speed of pumping increases, so does the prospect for a surge of pressurized air getting into the tank, which might end in over pressurization with normal venting. Now the usual for correct vent measurement in pneumatically loaded polyethylene tanks is double the dimensions of the fill; for example, a two-inch fill line means utilizing a four-inch vent. This permits the air to evacuate at a sooner rate, decreasing the danger for over pressurization.
Thus for such liquids which usually tend to flash or to boil, the venting necessities are double. The further 6 SCFH of air is predicated on 0.5 percent of liquids being evaporated and vented together with air. Process tanks and vessels working at low or atmospheric pressures are designed to deal with low pressures and enormous variation in strain can result in damaging these equipments.


















No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.